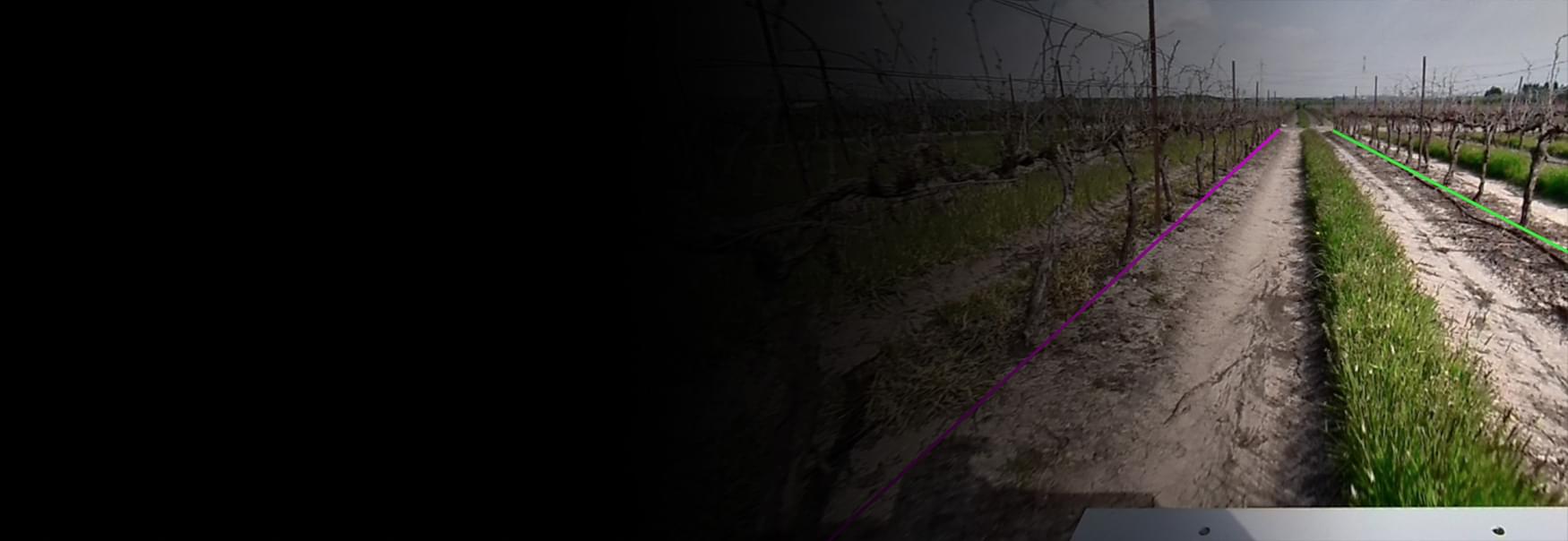
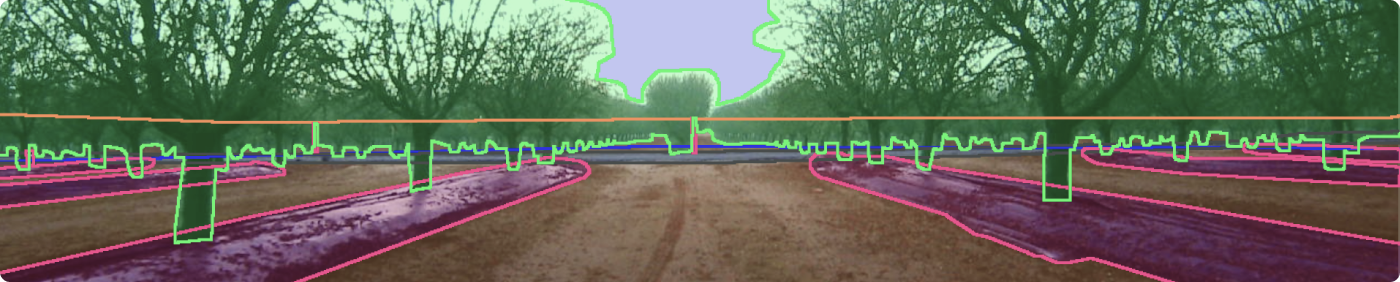
Bluewhite’s LiDAR data was in the form of sequences of the lidar channels (intensity, reflectivity, and range), where each pixel separately had various information, including the distance from the lidar. For annotation, this format was highly challenging: the images looked like “flat” pictures with no visual cues, making it nearly impossible to quickly understand which objects were closer to the tractor and which were farther away.
A particular challenge was that only objects within a specific range needed to be labeled. Anything beyond that was irrelevant for the model, so a custom solution was required.
Solution:
To adapt the data for 2D annotation, the Keymakr team developed a custom tool on the Keylabs platform:
-
Each depth range was assigned a distinct color (a gradient from red to green/blue).
-
The color scale was overlaid onto the LiDAR images, allowing annotators to see which objects fell into the required depth range immediately.
-
Clear rules were set: only objects of a specific color (i.e., within the defined distance) were to be labeled.
In effect, the team translated 3D information into a 2D space, making it easier and more efficient to process. This solution was created at record speed, allowing the labeling process to be completed quickly and efficiently.
Validation in Segments.ai:
Although all data annotation was performed in 2D, quality had to be confirmed in a 3D space. For this, Keymakr used Segments.ai, a partner platform specializing in 3D data workflows. Before export, results were uploaded into Segments, where the team verified how annotations mapped in 3D, checked for offsets or errors, and made adjustments where needed.
By working with Keymakr, Bluewhite accelerated the development of its perception systems while maintaining high accuracy and reliability. The 1.75–2x increase in annotation efficiency enabled Bluewhite to bring autonomy solutions to growers more quickly, helping them achieve safer and more productive operations in the field.